"Polypropylene (PP)"
is a thermoplastic polymer that is used in a wide range of applications including film and sheet, blow molding, injection molding, food packaging, textile, Laboratory and medical equipment, pipe, industrial and construction applications and automobile components are used. In addition, the polymer produced from propylene monomer is usually resistant to chemical solvents, bases and acids. The characteristic code of this polymer.
✴️ Polypropylene Applications ✴️
Polypropylene is the most important material of propylene derivatives, which accounts for about 61% of the total production of propylene. Polypropylene resins are widely used in the production of thermoplastic resins. Polypropylene is mostly used as a homopolymer, but recently its copolymer products are also growing. Injection molding (about 35% of global consumption): its most important uses include making car interior parts, medical syringes, plastic consumer products and packaging. The interior parts of the car that are made of polypropylene include: battery boxes, bumper plates, interior upholstery, interior door panels. Consumer plastic products include: plastic containers used in homes, plastic furniture, entertainment devices, tool boxes, Toys, packaging uses include covers and caps, hard containers and pallets, Chinese packaging boxes, liquid and solid medicine packaging. Production of fibers and fibers (about 30%): Its main use is in carpet and sack factories, and its other uses are in the production of bags and curtain fabrics. Its non-textile applications include: screw tape and strapping, decorative ribbons, etc. Production of film (about 19%): Polypropylene has replaced cellophane in many cases due to its transparency and moisture insulation. Film resins are basically used in food packaging, pressure-sensitive adhesive tapes, protective plates, confectionery and tobacco packaging.
Sack : It is a kind of rough fabric that is used to make durable and strong bags for carrying agricultural products such as potatoes and rice and the like. In the past, sacks were woven only from hemp and hemp fibers. Today, the same material is common, but more and more, woven sacks made of synthetic fibers such as polypropylene are replacing sacks made of natural fibers. Often, a bag made from a sack is also called a sack. The first sack weaving factory in Iran started in 1311 in Rasht. Polypropylene (polypropylene bag) is produced from the polymerization of propylene gas (propylene bag). The difference between the polypropylene molecule (PP) (propylene bag) and the polyethylene (PE) molecule (propylene bag) is only in an additional carbon atom in the gas monomer, and this different structure of the initial monomer causes more uniform side branches that are As a result, the resulting material has more uniform physical and chemical properties. The crystallinity of PP is lower than PE (propylene bag) and it is easier to produce it in an amorphous form. The production cost of PP (propylene bag) is low and its density is low and it is easier to process compared to PE. Its resistance to cold flow is better and its deformation is less at high temperatures. It has good tensile strength and surface hardness. PP (propylene bag) is more economical than PE under the same conditions. Its advantage is that it has a higher softening point, so it is used in making bottles that are filled with hot materials or exposed to heat. In the figure below, the propylene molecule (propylene bag) is shown. Medical equipment that is sterilized by steam is usually made with PP (propylene bag). Some cardboards are also coated with PP (polypropylene bags), which are used as liquid retainers for microwaveable food products. But it is not possible to use PE in this way due to its low softening point. The figure below shows the polypropylene molecule (propylene bag). High quality PP fabrics (polypropylene bags) are produced and supplied in rolls. Today, polypropylene fabrics (polypropylene bags) are used in many industries. The main use of these fabrics is to produce polypropylene and jumbo bags.
انی Polypropylene Bag Production Steps
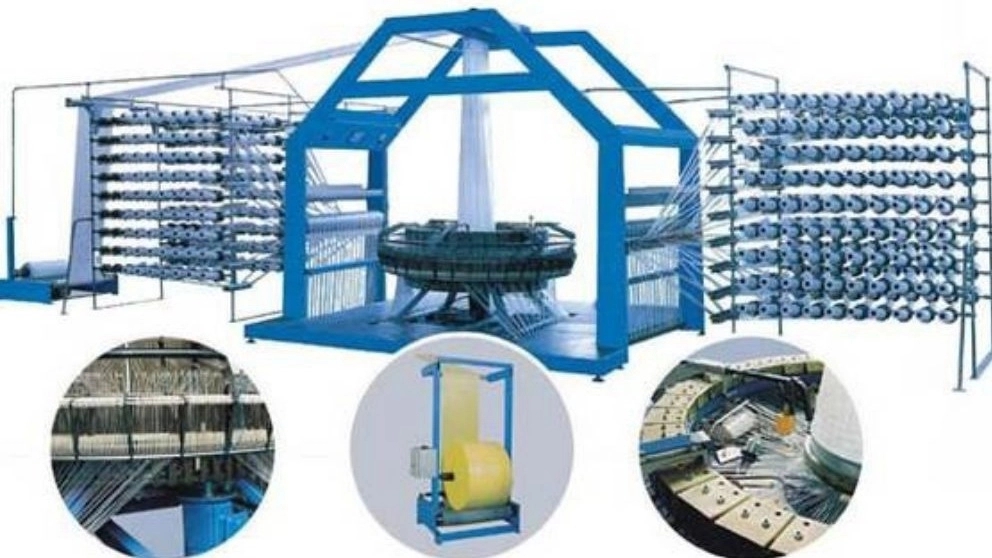
This product is produced and marketed in four main stages. These 4 steps are: :: Spinning stage
:: Weaving stage
:: Printing, cutting and sewing stage
:: Packaging
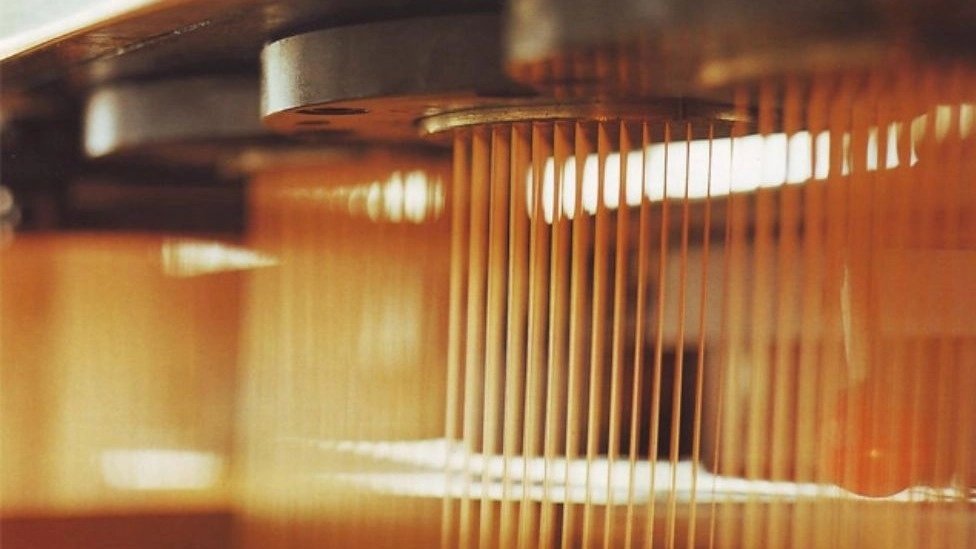
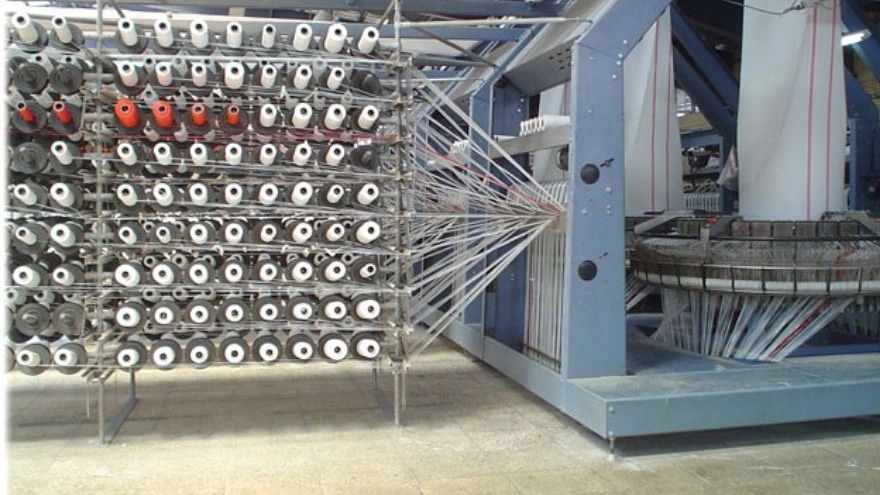
"spinning stage" To produce polypropylene yarns, firstly, polypropylene granules, masterbatch color and softening materials are fed to the machine, these materials are mixed in a chamber in proportion to each other, and then directed to the heating element and melted. . After passing through the heating element, it enters the pipe whose temperature has been reduced to 100 degrees Celsius by the hot oil pot, and after passing through the hot oil pot area, it goes to four showers, each of which has 64 holes, guided by air pressure and after passing With the pressure from the showers, it enters the cooling channel so that the strands keep their shape and state. The stretching of the threads is welded to each other and then it is wound on a bobbin, and after the bobbin is full, it is unloaded from the machine and wound on another bobbin, packed in plastic bags, and after weighing, it is sold in the market. /p>
Weaving stage In the weaving stage, the following actions are performed: - Weaving tape by knitting machine - Production of polypropylene sack rolls

In the weaving part, there are mainly three main methods for fabric production, which are: 1- Tari and weft weaving 2- Tari circular knitting 3- Weft ring weaving In this design, warp and weft weaving with a spinning machine is proposed. Production bags with the ring method are desirable for packing and transporting materials that have coarser grain size. Depending on the type of sack used, you should choose one of two methods for production.
"Cutting and sewing"
At this stage, roll the sack at the beginning of the cutting line. It is placed and cut according to the requested length by a thermal blade. The process of sewing the bottom of the sack is folded to the desired size and crocheted using a special sewing machine. "Packaging" Packing of sacks After counting 500 by hand or baling press, it is packed and marketed. In the weaving part, there are mainly three main methods for fabric production, which are: warp and weft knitting, warp and weft ring knitting, non-woven fabric production methods. For the production of polypropylene bags, so far, the non-woven method is created by creating layers and capturing fibers. come It has not been effectively used, but the method of circular weaving, tari and podi is used now. The bags produced by the two methods have different specifications and cannot be replaced. In this design, warp and weft weaving is proposed with round knitting machines, which constitutes the major part of domestic production and consumption. Ring production bags are desirable for packing and transporting materials with coarser grain size. Depending on the type of bag use. You should choose one of two methods for production. Circular knitting machines are divided into large or small diameter machines according to the size of the circumference, depending on the type of bag use, the desired machine diameter should be selected. In addition to that, the wefting speed of the machine, the number of makos and the entry of the machine and the wefting system should be taken into consideration in choosing the machine.
In the spinning part, the film of lead extruders is usually made in two ways: blowing or flat, the flat system has better quality and this method is used in this design.
Another difference in the spinning part is the method of cooling the film, which is usually done in two ways. Either by hot water or by a roller through which cold water passes, in the first method, the yarn is stronger because the cooling time is fast and the formation of crystals is prevented, and the optimal method is the hot water tub method. Is.
Another difference in spinning machines is the yarn stretching part, which is done by hot air when the yarn passes through the hot plate, and the yarn stretching using hot air increases the quality of the yarn due to the lack of friction on the metal surface.


