What is a compressor?
"Gas Compressor" (Gas Compressor) is a mechanical device that increases gas pressure by reducing volume. Compression of gas naturally increases its temperature. Compressors are similar to pumps in that they increase the fluid pressure and cause the fluid to move inside the pipe. Since gases are compressible, the compressor can reduce the volume of the gas; This is despite the fact that liquids are relatively incompressible and receive the required energy from a pump. Pumps in incompressible fluids lead to fluid flow in pipelines.
Gas compressors for a wide range of applications including: natural gas transmission through pipelines, storage of pure gases in small volumes, air compression Intakes are used in gas turbines, pressurized aircraft cabins, heat transfer in refrigeration systems, air storage in submarines, and compressed air supply for air-operated brakes.Types of compressors
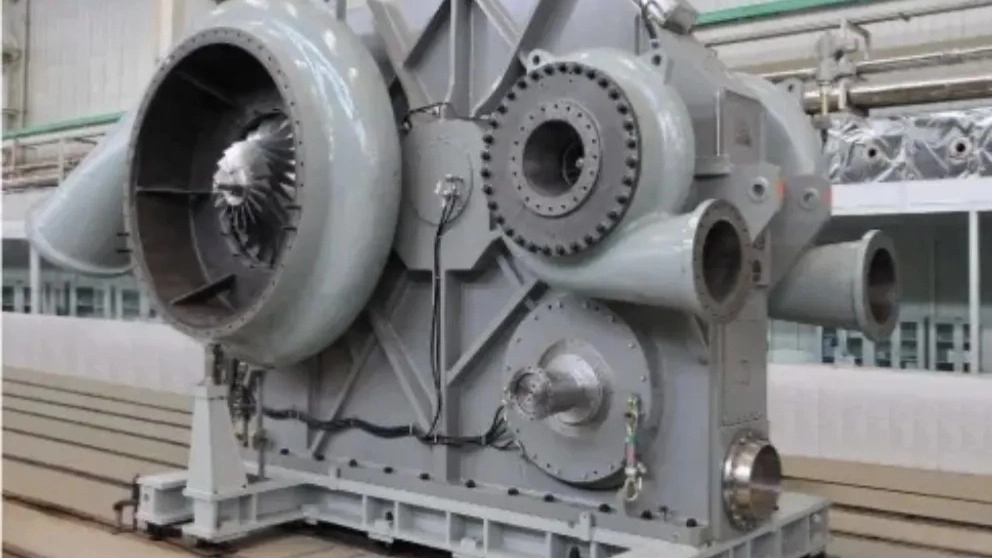
Centrifugal compressors "Centrifugal compressors" use a rotating disk or an impeller that is located in a chamber to direct the gas to the edge of the impeller and increase the speed of the gas. "Diffuser" or the diverging channel converts the energy caused by the speed into pressure energy. This category of compressors are mainly used for continuous service in industrial fields such as oil refineries, chemical plants and natural gas process petrochemicals. In the figure below, you can see a type of multistage centrifugal compressor.
The application range of centrifugal compressors can be extended from 100 horsepower (75 kW) to 1000 horsepower. Multistage compressors can produce very high output pressures (over 10,000 pounds per square inch) to drive fluid. Many large snow machines (such as ski resorts) use this type of compressor. These equipment are also used in "Internal Combustion Engines" as "Superchargers" and "Turbochargers". Centrifugal compressors are used in small gas turbine engines or as the last stage of compression in medium-sized gas turbines.
Mixed flow compressors Mixed-flow compressors are similar to centrifugal compressors, but in addition to the radial speed, they also have an axial speed at the exit from the rotor. Often, a diffuser is used to convert the mixed flow into an axial direction. The diameter of the diffuser of the mixed flow compressor is smaller than that of the radial flow compressor.
Axial flow compressors Axial-flow compressors use a fan-like rotating blade to compress the gas flow. Fixed blades attached to the body after each moving vane direct the flow onto the next set of moving vanes. The passing gas level decreases along the compressor to keep the "Mach Number" constant. Axial flow compressors are typically used in high flow applications such as medium and large gas turbo engines. These equipments are usually multi-stage. At design pressure ratios higher than 1 to 4, variable geometry is often used to improve performance.

Reciprocating compressors Reciprocating compressors use a moving piston with a crankshaft. They can be either fixed or portable, single-stage or multi-stage, driven by electric motors or internal combustion engines. Small reciprocating compressors from 5 to 30 horsepower are commonly used in automotive applications and are usually used for a variety of tasks. Larger reciprocating compressors up to 1000 horsepower are commonly found in large industries, but their numbers are decreasing over time and being replaced by other compressors. The outlet pressure can range from low to very high pressures (over 5000 psi or 35 Mpa). In some special applications, such as air compression, multistage double-acting compressors are more efficient and typically larger, noisier, and more expensive than centrifugal compressors.
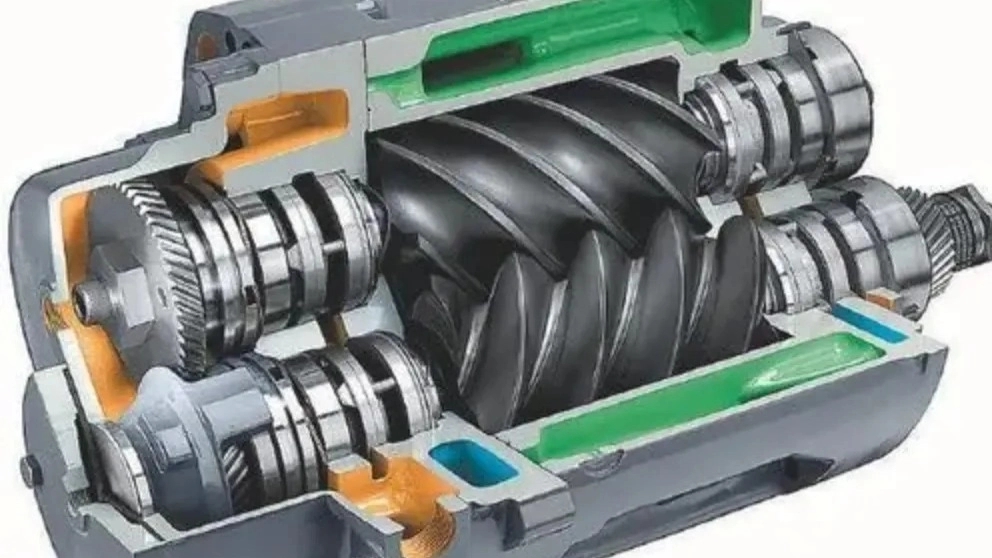
Screw compressors "Rotary Screw Compressors" use two circular spirals to move gas into a smaller space. They are commonly used for continuous flow in commercial and industrial applications and may be fixed or portable. Their applications can range from 3 HP (2.24 kW) to over 500 HP (375 kW) and from low pressure to very high pressure (1200 psi or 8.3 Mpa). This equipment is usually used to supply air to precision instruments. This type of compressor is also used for many car engine superchargers because it is easily compatible with the induction capacity of a piston engine.

Spiral compressors The "scroll compressor" (spiral), also known as the "scroll pump" and "scroll vacuum pump", uses two identical spiral shaft blades to Help compress liquids and gases. The geometry of the blade may be involute, Archimedean spiral or combined curves. This type of compressor works more easily, more quietly and more reliably than other types of compressors. Often one of the scroll blades remains stationary while the other moves eccentrically; Through this, the fluid is pumped or compressed between two blades.
Diaphragm compressors "Diaphragm compressor" (diaphragm compressor) which is also known as a "membrane compressor" (membrane compressor) is a type of reciprocating compressor. Gas compression is done by moving the flexible diaphragm. The back and forth movement of the diaphragm is done by a rod and a crank mechanism. Only the diaphragm and the compressor box are in contact with the compressed gas.
Diaphragm compressors are also used for hydrogen and compressed natural gas (CNG). Pictured in this section is a three-stage diaphragm compressor designed to compress hydrogen gas to 6,000 PSI, or 41 MPa, for use in a prototype hydrogen and compressed natural gas (CNG) refueling station in downtown Phoenix, Arizona by Arizona Public Utilities (a Electric Installation Company) has been built. For the prototype fueling station, reciprocating compressors were used to compress natural gas. The prototype replacement gas station was built in compliance with all safety, environmental and building codes in Phoenix to demonstrate that such gas stations can be safely built in urban areas.

